The limitations of blockchain technology have become more obvious as it develops. Network fragmentation, scalability, and interoperability have made it difficult for developers, users, and businesses to take advantage of decentralized solutions. Although Layer 1 blockchains, such as Ethereum and Solana, seek to address security and scalability issues within their own ecosystems, they frequently function independently and are unable to effectively communicate with one another.
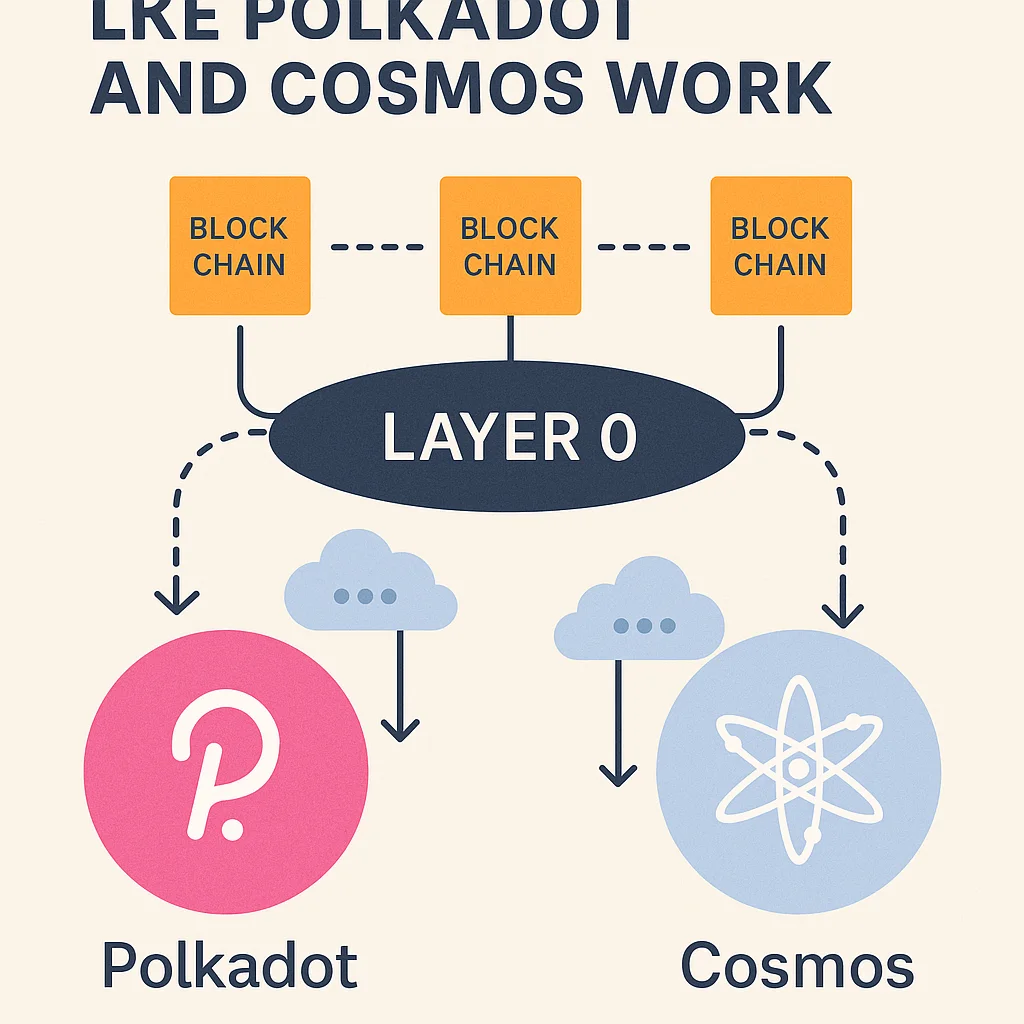
Layer 0 protocols such as Cosmos and Polkadot are introduced. In addition to providing the underlying technology for a multi-chain, interconnected Web3 future, these foundational blockchain infrastructures seek to address the interoperability issue. Layer 0s offer a structure that allows several Layer 1 blockchains to function together, as opposed to being individual chains with their own consensus and smart contracts.
We'll explain Layer 0 protocols, Polkadot and Cosmos operations, and the significance of these networks for the development of decentralized technology in this blog.
What Is a Layer 0 Protocol?
The foundational infrastructure that makes it possible to create and connect multiple blockchains is referred to as Layer 0 in the blockchain tech stack.
Here’s how the blockchain layers stack up:
-
Layer 2: Scaling solutions like Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups
-
Layer 1: Blockchains like Ethereum, BNB Chain, Solana
-
Layer 0: Frameworks that enable multiple Layer 1 chains to exist and communicate (e.g., Polkadot, Cosmos)
Layer 0 protocols provide:
-
A base layer for building custom blockchains (Layer 1s)
-
Cross-chain interoperability
-
Shared security or consensus (in some models)
-
Modularity and flexibility
Layer 0 permits independent, interoperable chains with distinct goals and regulations rather than imposing all apps onto a single chain.
Why Layer 0 Is Important
1. Solves Interoperability
Conventional blockchains don't communicate with one another. A universal framework for chain-to-chain communication is established by Layer 0s.
2. Enhances Scalability
Layer 0 lessens bottlenecks on any one network by distributing computation and transactions across several chains.
3. Supports Customization
Developers can launch purpose-built chains with their own tokens, governance, and logic.
4. Strengthens Ecosystem Development
Layer 0 fosters ecosystems of interconnected blockchains, rather than siloed applications.
Polkadot: A Layer 0 Built on Shared Security
Overview:
Gavin Wood, a co-founder of Ethereum, developed Polkadot, a Layer 0 platform that uses a central relay chain to link several specialized blockchains known as parachains.
Token: DOT
Consensus Mechanism: Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS)
Launch Year: 2020
Key Components of Polkadot
1. Relay Chain
-
The heart of the Polkadot network
-
Responsible for security, consensus, and cross-chain communication
-
Does not support smart contracts itself
2. Parachains
-
Independent Layer 1 blockchains connected to the Relay Chain
-
Optimized for specific use cases (e.g., DeFi, NFTs, gaming)
-
Can have their own governance and tokens
3. Bridges
-
Enable communication with external blockchains like Ethereum and Bitcoin
-
Crucial for cross-ecosystem interoperability
4. Parathreads
-
Similar to parachains but on a pay-as-you-go model
-
Ideal for smaller projects that don’t need constant connectivity
How Polkadot Works
Polkadot uses the Relay Chain to offer shared security. The main network's security is available to all parachains, saving them from needing to bootstrap their own validator set. DOT-staked validators guarantee network consensus.
In order to facilitate smooth cross-chain communication, parachains send block candidates to the Relay Chain through collators, and validators complete these blocks.
Use Cases and Ecosystem
Notable parachains include:
-
Acala: A DeFi hub with a stablecoin and liquidity staking
-
Moonbeam: A smart contract parachain compatible with Ethereum
-
Astar: Multi-VM platform supporting WASM and EVM
Polkadot’s ecosystem is growing rapidly with a focus on specialization and collaboration.
Cosmos: A Layer 0 Built on Sovereignty
Overview:
As the "Internet of Blockchains," Cosmos offers a communication protocol and SDK for creating and integrating separate blockchains.
Token: ATOM
Consensus Mechanism: Tendermint BFT
Launch Year: 2019
Key Components of Cosmos
1. Cosmos SDK
-
An adaptable structure for creating blockchains
-
provides plug-and-play modules for token creation, governance, and staking.
-
used to create well-known chains such as Secret Network, Osmosis, and Terra
2. Tendermint Core
-
A consensus engine that can tolerate Byzantine faults
-
keeps the application logic apart from the networking and consensus layers.
-
guarantees low latency and quick finality.
3. IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) Protocol
-
Cosmos’s flagship feature
-
Enables different Cosmos-based blockchains (zones) to transfer tokens and data
-
Designed for trustless, decentralized cross-chain communication
How Cosmos Works
Cosmos prioritizes sovereignty over shared security, which sets it apart from Polkadot. Every chain, referred to as a zone, operates independently with its own validators and regulations.
These zones are connected to a central hub called Cosmos Hub, which uses the IBC protocol to enable cross-chain transfers. Cosmos zones are independent of a central relay chain for security and consensus, in contrast to Polkadot.
Use Cases and Ecosystem
Some major projects built on Cosmos include:
-
Osmosis: A decentralized exchange using IBC for liquidity sharing
-
Terra (pre-collapse): An algorithmic stablecoin ecosystem
-
Secret Network: Privacy-preserving smart contracts
-
Kava: A DeFi platform with cross-chain lending
Cosmos continues to attract developers looking for modularity, sovereignty, and interconnectivity.
The Future of Layer 0 Protocols
Layer 0 protocols will become essential in bringing the blockchain universe together as the Web3 ecosystem grows. What to anticipate is as follows:
1. Cross-Ecosystem Bridges
more sophisticated and safe bridges that link Layer 0s with Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana.
2. Composability
dApps on one chain will be able to initiate actions on another through projects like XCM (Polkadot) and Interchain Accounts (Cosmos).
3. Layer 0 Interoperability
Polkadot and Cosmos are being connected in order to create a fully connected Web3 world.
4. Developer Ecosystem Growth
Simplified toolkits, better documentation, and funding will bring more talent into Layer 0 development.
Challenges Facing Layer 0 Protocols
1. Complexity
Building and maintaining cross-chain communication and security mechanisms is difficult and resource-intensive.
2. Security Risks
Bridges and shared security models are prime targets for hackers.
3. Fragmentation
With multiple Layer 0s emerging (Avalanche Subnets, Ethereum Rollups, etc.), the ecosystem could become even more splintered.
4. Adoption Hurdles
Getting developers and users to shift away from established Layer 1s can be challenging.
Final Thoughts
Polkadot and Cosmos aren’t just competitors—they represent two philosophical approaches to the future of blockchain.
-
Polkadot believes in shared security and unified governance.
-
Cosmos emphasizes sovereignty and modularity.
These two titans of Layer 0 are working to address the three main issues with blockchain: specialization, interoperability, and scalability. These networks are establishing the groundwork for an internet of blockchains, where data, tokens, and applications freely move throughout a decentralized world, as the cryptocurrency space expands.


Leave a Reply