Private keys are the most important factor that establishes security and ownership in the realm of cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrencies function on a decentralized network, in contrast to traditional banking, where your money is protected by a centralized organization. This implies that safeguarding your possessions is your responsibility and your responsibility alone.
You will never be able to access your cryptocurrency again if you lose your private key. In a similar vein, if someone else manages to obtain your private key, they can immediately embezzle your money and leave you unable to get it back.
This blog post will explain private keys, their significance, and safe storage practices to safeguard your digital assets.
1. What is a Private Key?
A lengthy, randomly generated string of alphanumeric characters known as a private key serves as a password for controlling and gaining access to your money. Your wallet address is generated by a public key that is mathematically connected to it.
Example of a Private Key:
E9873D79C6D87DC0FB6A5778633389A46C2A93E5B8A8FDEC3E8D0E4F8E4A1E8A
You can prove ownership of your digital assets and sign transactions with this special code.
Public Key vs. Private Key
| Feature | Public Key | Private Key |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Used to receive funds | Used to access and send funds |
| Visibility | Can be shared with others | Must be kept secret |
| Generation | Derived from private key | Randomly generated |
| Security | Safe to share | If compromised, assets can be stolen |
💡 Think of it this way: The private key is like your email password, which needs to be kept hidden, while the public key is like your email address, which is safe to disclose.
2. Why Are Private Keys Important?
Since cryptocurrencies are decentralized, private keys serve as the only way to access and control funds.
✔ Full Ownership – Private keys allow you total control over your possessions, unlike banks where third people manage your money.
✔ Security Against Fraud – By limiting who can approve transactions, private keys lower the possibility of unwanted access.
✔ No Recovery If Lost – Unlike banks, where forgotten passwords can be reset, you cannot get your money back if you lose your private key.
🚨 Important: Your money can be stolen right away and the transaction is irreversible if someone else manages to obtain your private key.
3. How Private Keys Can Be Compromised
Private keys are secure, but if not handled correctly, they can be stolen. Here are a few typical dangers:
A. Phishing Attacks
Cybercriminals trick users into revealing their private keys through fake websites or emails.
💡 Example: You receive an email claiming to be from a crypto exchange, asking you to enter your private key.
B. Malware & Keyloggers
Hackers use malware to track keystrokes and steal private keys stored on computers or mobile devices.
💡 Example: downloading a program that discreetly stores your private key in a false wallet.
C. Weak Passwords
Hackers can easily obtain your private key if you use a weak password or keep it in an unencrypted file on your computer.
💡 Example: storing your private key on your desktop as the "CryptoKeys.txt" text file.
D. SIM Swapping
In order to reset wallet passwords and obtain private keys, hackers take over your phone number.
💡 Example: Your money could be stolen by a hacker who takes over your phone number if your cryptocurrency wallet permits SMS-based recovery.
E. Physical Theft
Someone can access your money without your equipment if you write down your private key and they manage to take it.
4. Best Ways to Secure Your Private Keys
To protect your cryptocurrency, follow these best security practices:
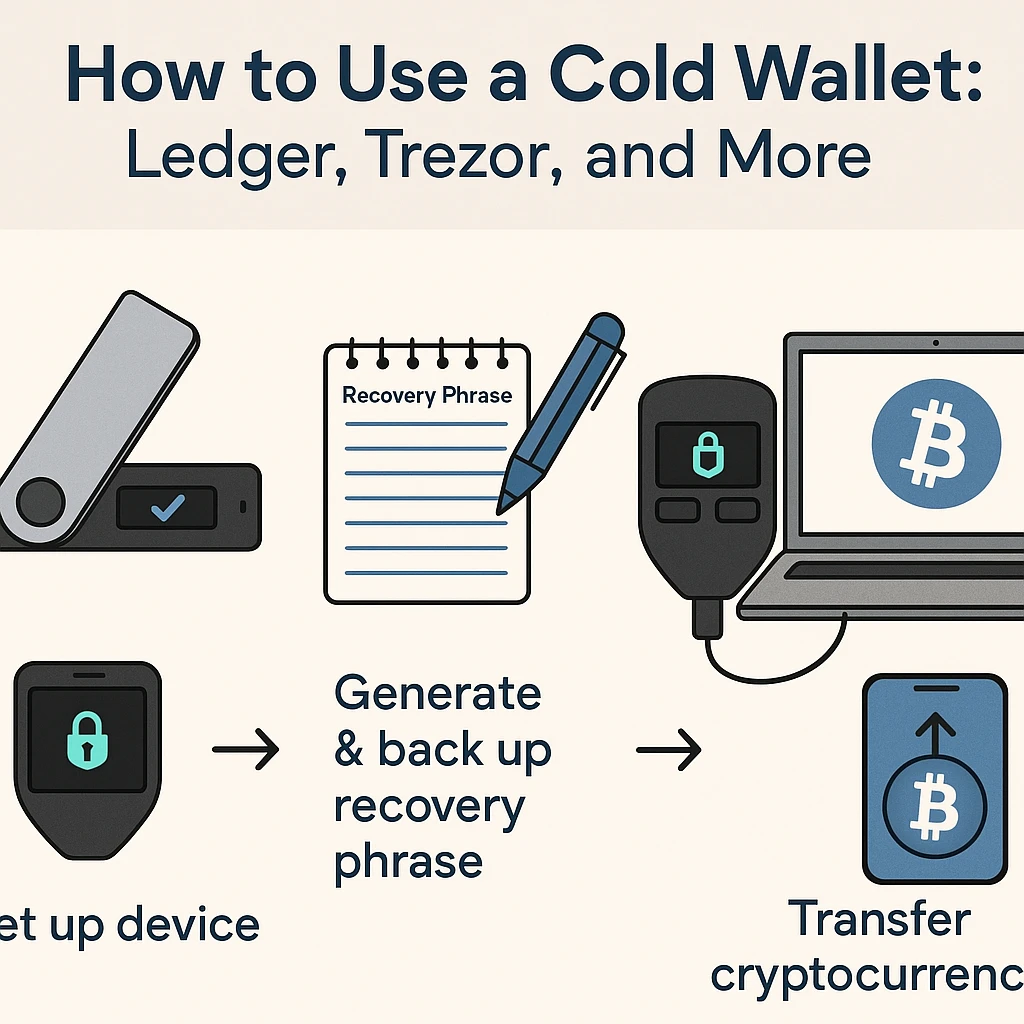
A. Use Hardware Wallets (Cold Storage)
Your private keys are stored offline in a hardware wallet, which is a physical device that is impervious to hacking.
✔ Safe from online attacks (malware, phishing).
✔ Can be connected to any device to sign transactions securely.
✔ Examples: Ledger Nano X, Trezor Model T.
💡 Tip: To prevent hacked devices, only purchase hardware wallets from authorized vendors.
B. Store Private Keys on Paper (Paper Wallets)
You may defend your private key against online attacks by writing it down and keeping it in a safe location.
✔ No risk of digital hacking.
✔ Safe if stored securely.
🚨 Risk: If lost, damaged, or stolen, your funds are gone forever.
💡 Tip: Keep copies in several safe places, like a safe deposit box.
C. Use Multi-Signature Wallets
An additional degree of protection is added by requiring numerous private keys in order to authorize a transaction in a multi-signature wallet.
✔ Prevents a single point of failure.
✔ Ideal for businesses and high-value accounts.
💡 Example: To authorize transactions, a cryptocurrency investment company might need three of every five private key holders.
D. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
To avoid unwanted access, use 2FA for cryptocurrency wallets and exchanges.
✔ Use Google Authenticator instead of SMS-based 2FA.
✔ Reduces risk of SIM swapping attacks.
💡 Tip: Write down your 2FA backup codes instead of storing them online.
E. Avoid Storing Private Keys on Digital Devices
Private keys should never be kept in unencrypted files, online storage, or emails.
🚨 Hackers can access them if your device is compromised.
💡 Tip: If you must store them digitally, use encrypted USB drives.
5. Role of Temporary Emails in Private Key Security
You frequently need to enter your email address when registering for cryptocurrency wallets, exchanges, or DeFi platforms. You can lower risks and safeguard your identity by using temporary email services like Free Temp Mail, mytemp-mail, and 10minutesmails.
✔ Avoid Spam & Phishing – Stops unsolicited emails from exchanges that might contain phishing links.
✔ Protect Your Privacy – Prevents hackers from connecting your wallet and email.
✔ Temporary & Disposable – lessens the risk of data breaches.
💡 Tip: Never link your primary cryptocurrency accounts to temporary emails; instead, use temporary emails when registering for crypto services.
6. What Happens If You Lose Your Private Key?
Regretfully, losing your private key results in the permanent loss of your money. Nevertheless, if you have a backup, you can restore access in the following ways:
✔ Check for a Recovery Phrase – A 12–24 word seed phrase that can restore your money is generated by many wallets.
✔ Look for Backups – Get your private key from a backup device if you encrypted it and kept it safe.
✔ Seek Expert Help – Although recovery of lost keys is a specialty of some crypto forensics firms, success is not assured.
🚨 If you don’t have a backup, your funds are permanently inaccessible.
Final Thoughts
The security of cryptocurrencies is based on private keys. You can't manage your money without them. Strong security procedures, such as the use of hardware wallets, multi-signature protection, and avoiding online storage, are necessary to keep them safe.
When signing up for crypto-related services, using temporary addresses (10minutesmails, mytemp-mail, Free Temp Mail) might provide an additional degree of security. But always make sure you use a very secret and safe email for your primary cryptocurrency accounts.
🔐 Your private key = Your financial future. Protect it wisely! 🔐



Leave a Reply